motional eating, also called stress eating or emotional overeating, is defined as eating/overeating in response to negative emotions. Such overeating is not good for your well-being as excess energy intake inflicts physical as well as mental impact, and people taking weight loss medication find it hard to relinquish extra fat due to emotional eating disorders. On the other hand, genuine hunger inspires you to curb your cravings and be selective about the quality and quantity of food items in order to control your body weight. If you wish to maintain your body weight or avoid obesity, in that case, it is essential to learn the difference between emotional eating vs real hunger, as well as how to overcome emotional eating to live a life free from its negative effects.
Mechanism of hunger
Hunger is a physical sensation that drives you to take food, so the absence of any such sensation indicates you are not sufficiently hungry. The craving for food is primarily regulated by the hypothalamus, a brain region that integrates various signals related to energy balance. The entire process involves endocrine, neuroendocrine, and metabolic signals that influence hunger and satiety.
The key factors that regulate your hunger are Ghrelin, Leptin, Hypothalamus, Vagus Nerve, Migrating Motor Complex, and Gut Microbiota. Those who take weight loss medication or are looking to reduce excess fat understand every aspect of natural hunger and know when and how much food is needed to satisfy their appetite.
Emotional eating vs real hunger
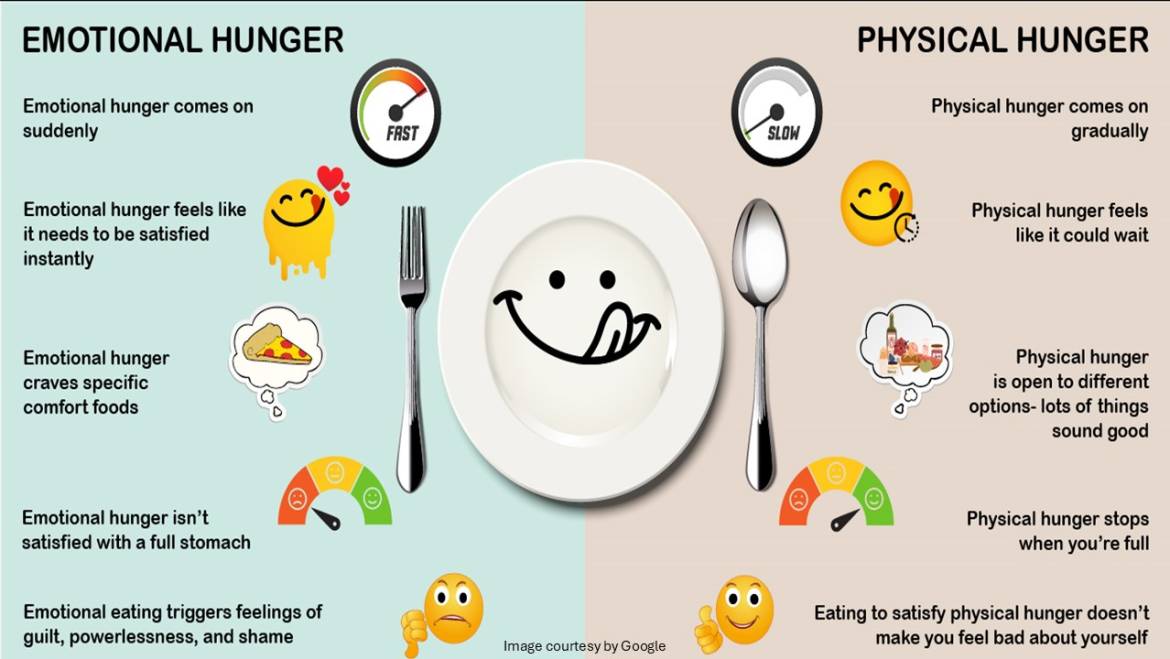
A fitness enthusiast creates a well-planned diet chart in consultation with a health expert. Usually, emotional eating does not feature on their menu; rather, they prefer to stick to true hunger. The term true hunger or physical hunger denotes the feeling of hunger in response to your body’s biological need for food. Under the sensation of true hunger, you take the amount of food products that your body needs in order to stay healthy and lively. In fact, true hunger supports your weight loss efforts, and you feel good internally after adopting this food regime. You may have seen many celebrities who lose pounds of extra fat within a few months to stay slim and fit as well. They never recommend you to indulge in emotional eating that may raise some unwanted health issues.
The same results are not expected with emotional eating, as this habit can sabotage your weight loss efforts. Excess intake of food under emotional eating leads to excess accumulation of high calories and fat around the vest. It starts with cravings for specific comfort food products, such as deep-fried, spicy, packaged, or flavoured items. Sometimes, people pretend to be in stress as an excuse for overeating to feel relieved. Some cases are also found where emotional eating disorder is treated as a part of the lifestyle. In such cases, people often believe that the more you eat, the stronger you become, whereas dieting makes you physically weaker.

Emotional eating and its symptoms?
Emotional eating often begins as a way to cope with emotions rather than satisfy physical hunger. For example, many people often eat ice creams or desserts after breaking up with their partners. Similarly, many people eat cookies and bakery items while dealing with family-related issues or stress. Any emotional incident, whether it is work stress, health issues, relationship struggles or financial worries, can trigger a desire to eat anything even if your body does not need it. In other words, stress can override appetite, and your mental state craves something extra; this situation can create an artificial hunger.
There are some common triggers of emotional eating, such as:
-
- Stress-related to work, personal relationships, career, education, or family matters
- A feeling of social ignorance
- Anxiety or depression
- Loneliness or boredom
- Habit for eating junk foods
- Eating popcorn or fast foods while watching TV or mobile
- Celebrations or family/office events that push you to taste more and eat more
How to overcome emotional eating?
One can overcome emotional eating in various ways, but before doing so, it is essential to understand your eating habits. You should know what triggers your eating habits. Make a list or record the times when you feel like eating emotionally but realize you are not physically hungry. Once you identify the emotions, thoughts, and situations that trigger you to eat more, you can make changes accordingly. Things that can help overcome emotional eating include taking a walk, playing with your pet, listening to music, reading books, practising mindfulness or meditation, spending time with family and friends, joining a sports activity you enjoy, adding protein to your diet, and removing tempting foods from your fridge and kitchen
Conclusion:
Your emotional condition has a good impact on your food preferences. Some studies have also found that physical or emotional stress increases cravings for foods or items high in fat and sugar. But you should learn how to overcome emotional eating if you want to maintain a healthy body weight. The distinction between emotional eating and real hunger can help you understand an ideal weight loss diet and healthy practices.