Almost everyone wishes for clean, spotless, healthy skin. Few are really lucky to have beautiful skin; they do little skin care, and it’s all done for them. On the other hand, some people require extensive skin care but still don’t achieve the results they desire.
Melasma, acne, eczema, etc., are some of the common skin issues that rob your face of its charm. This blog page covers information on what is melasma, the cure of melasma, what causes it, how to remove melasma and more; however, consulting a dermatologist is important to identify the treatment that suits your skin type.
What is melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes brown or gray-brown patches on the face or, less commonly, on the body. It is a form of hyperpigmentation caused by overactive pigment-producing cells. Though this condition is not dangerous, it can cause frustration and persist for a long time if not treated.
Common areas affected by melasma include the cheeks, forehead, nose bridge, upper lip, chin, and, sometimes, the forearms, neck, and waist.
What causes melasma?
Melasma occurs when pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) become overactive, leading to excess melanin production. What causes melasma can vary from person to person, as several triggers can overstimulate these cells; the common ones include:
1. Sun exposure – This is one of the most common causes of melasma. UV rays stimulate melanocytes. If your skin is prone to melasma, even a few minutes of sun rays can darken your skin.
2. Hormonal changes – Hormones like estrogen and progesterone can trigger melasma. The common hormonal triggers are pregnancy, birth control pills and HRT (hormone replacement therapy).
3. Genetic factor – If your family has a history of melasma, your melanocytes may be naturally more active.
4. Heat and harsh light – Not just UV; heat, harsh light, and infrared can also worsen melasma, e.g., hot showers, cooking over heat, outdoor exercise, and strong blue light from screens.
5. Skin irritation and inflammation – Over-exfoliating, using harsh skin products, or skin issues like eczema can lead to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, worsening melasma.
6. Certain medicines and products – Some medications, such as antibiotics and anti-seizure medications, perfumes, or skincare ingredients, can increase sun sensitivity or pigmentation.
7. Thyroid (less common) – Some research shows a link between melasma and thyroid disorders.
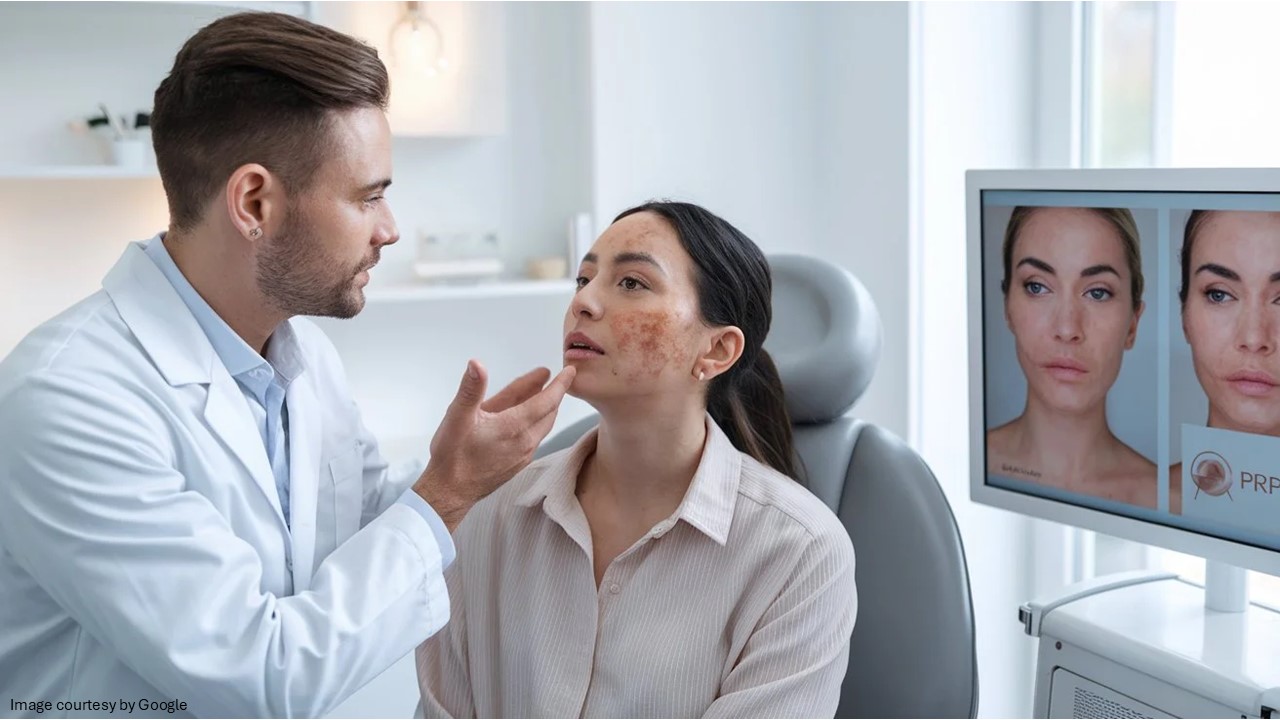
What does melasma look like, and what is the difference between melasma and other dark spots?
Identifying melasma among other dark spots is important for the right treatment and cure of melasma. So, let’s dive into how to identify the difference:
1. Melasma – Usually triggered by sun exposure, hormones, heat and genetics
Other dark spots – medication reactions, skin injuries, sun damage, post-inflammatory pigmentation.
2. Appearance of melasma – They are symmetrical, appear in large patches, not a single spot, with brown to grey brown or bluish in color, specifically on cheeks, forehead, upper lip, nose and chin area.
Appearance of other dark spots – They are usually tiny, scattered, asymmetrical, and can appear anywhere on the body, often following acne or skin irritation.
3. Skin depths of melasma – They are deep, epidermal, mixed and not easy to treat. Melasma patches are usually chronic and long-term, coming and going depending on the trigger.
Skin depths of other dark spots – Not that dark, often temporary, look more superficial, and fade away when treated rightly.
4. Treatment response – Melasma needs a gentle, long-term combination treatment. They can be easily worsened by laser, heart, or irritation and require strict daily sun protection. On the other hand, other dark spots often respond faster to chemical peels, laser treatments, spot treatments, and strong exfoliants and are not affected by hormonal changes.
5. The target population – 90% of melasma cases occur in women, especially those with medium to dark skin tones. At the same time, other dark spots can affect anyone, often related to sun damage, acne, and ageing.
What helps melasma?
The cure of melasma is manageable; it tends to be chronic and comes and goes. The consistent treatment and strict sun protection can significantly lighten it. Speaking to a dermatologist is recommended; she will assess the severity of your melasma and prescribe the formulation and strength of the medicine accordingly. Do not stop the treatment in between, even if you start to notice noticeable changes. Following the prescribed treatment duration is important to experience the desired result.
Some of the most common topical formulations for melasma treatment include hydroquinone, tretinoin, azelaic acid, kojic acid, tranexamic acid, and vitamin C. Most topical formulations work best when applied 30 minutes before bedtime.
Another natural way to treat melasma is sun protection. Yes, the most important treatment for melasma is sun protection.
Many people see a 50–70% improvement just from proper sun protection. Ensure to apply:
• Broad-spectrum SPF 30–50+
• Tinted mineral sunscreen
• Reapply every 2–3 hours when outside
• Avoid direct sun, especially midday
• Wear a wide-brim hat + sunglasses
• Avoid overheating the skin
• Manage hormonal triggers where possible
Melasma can improve a LOT with the right combination of daily habits and topical treatments.
Takeaway
Melasma can steal your skin’s beauty. Why allow melasma to persist when simple treatments and natural precautions can keep it at bay? Protect your skin from UV rays; wear protective clothing when going out in the sun. Consult a doctor to determine how to remove melasma when it comes and goes, and to identify the right topical formulation for your skin type.



