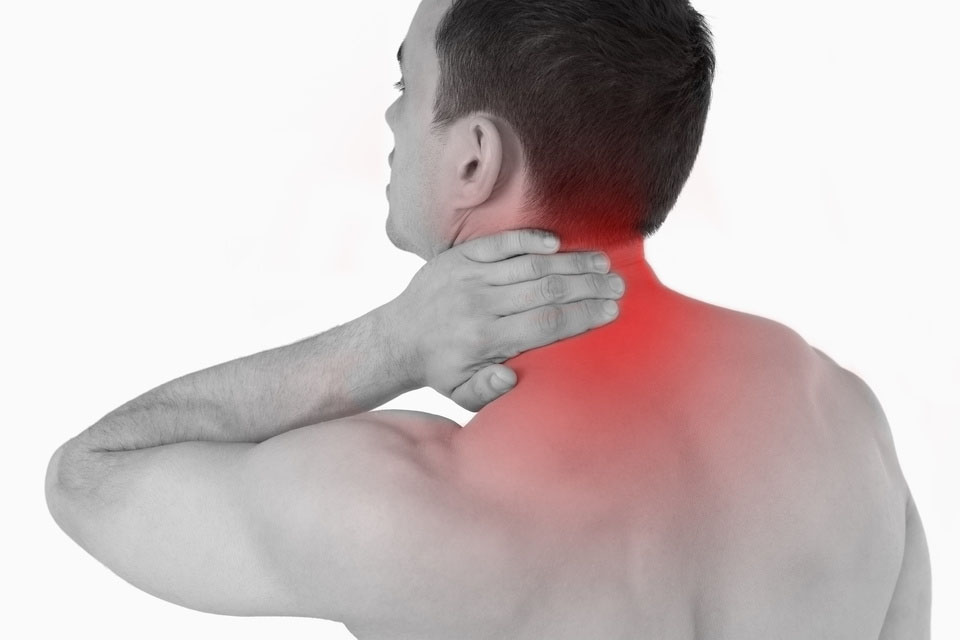
Muscle pain is extremely common, and everyone experiences muscle discomfort at some point. The pain can be experienced anywhere in the whole body as the whole body is covered with muscles. Overuse or injury is one of the possible explanations for ongoing discomfort.
There is a difference between acute pain and chronic muscle pain. Acute pain develops after a workout which does not last only a day or two. Chronic muscle pain usually persists for at least three to six months. However, these numbers are only guidelines, as we may identify a potentially chronic problem after a month or two.
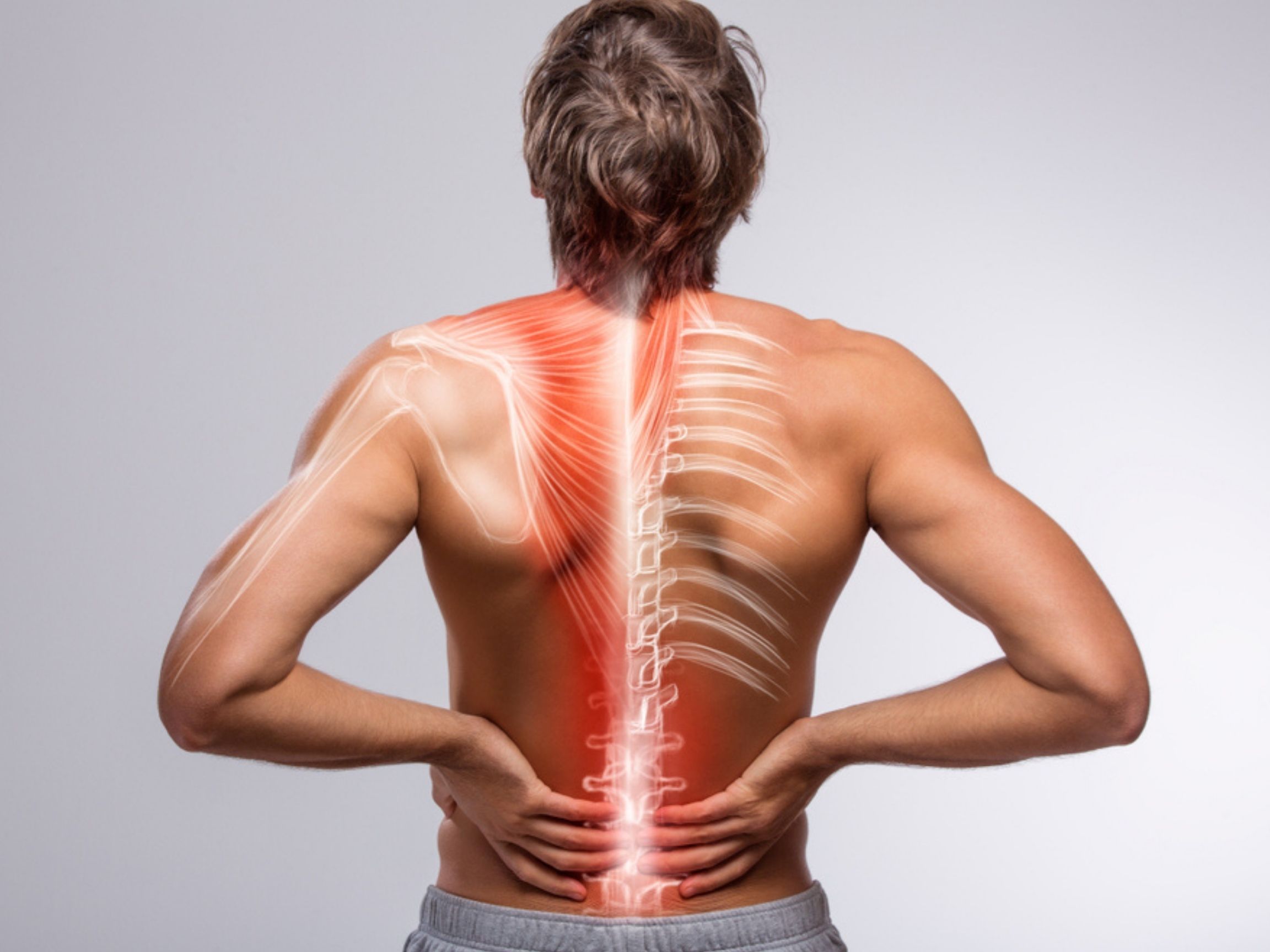
Reasons
There are two major reasons behind chronic muscle pain-
- Exertional compartment syndrome – there are different compartments in your limbs which are sets of muscles, nerves, and blood vessels covered by a tough tissue called fascia. If there is swelling or bleeding within one of these compartments, this leads to pressure leading to great discomfort in the muscles.
- Myofascial pain syndrome – The tough covering muscle fascia becomes inflamed, leading to muscle pain and discomfort.
What are the causes of chronic muscle pain?
Many chronic pain cases are associated with a specific injury that takes a long time to heal, for example, a surgical incision or a severe infection. At the same time, other incidents have no clear cause, prior nerve damage, or injury. However, any chronic cases are associated with lower back pain, fibromyalgia, shingles, nerve damage, headache, or osteoarthritis. Treating any of these conditions is extremely important when managing chronic pain.
When the pain does not resolve, it requires treatment that can address the patient’s physical and psychological health. One of the common causes of chronic pain is an initial injury such as pulled muscle or back sprain. During the condition, it is believed that pain develops after the nerves become damaged. Neuropathy or nerve damage increases the severity of pain and makes it long-lasting. In these cases, focusing on the underlying with an appropriate treatment approach is insufficient to control chronic pain.
As mentioned above, some people experience chronic pain without prior injury or apparent reason. The exact reason behind chronic pain without injury or nerve damage is to remain a topic of debate. The pain may result from an underlying condition such as chronic fatigue syndrome, endometriosis, inflammatory bowel disease, temporomandibular joint disease (TMJ), or intestinal cystitis.
Symptoms of chronic muscle pain
Symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness
- Muscle spasms
- Redness or bruising
- Muscle weakness
- Limited motion
- Swelling
The pain worsens with activity or stress. Patients can experience depression, fatigue, and behavioral disturbances.
Home remedies for easing muscle pain
Muscle pain often responds well to home treatment. They are not the ultimate solution, but they can relieve temporary pain.
Remedies are as follows-
- Allowing rest to the area of the body which pains
- Applying ice to the affected area to help relieve pain and reduce inflammation
- Gently stretching the muscles
- Avoiding high-impact activities
- Yoga and meditation to relax the tensed muscles
Do visit the doctor if the pain persists for a longer duration. Home remedies are a temporary solution; permanent solutions are with doctors only.
Treatment
There are over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen and naproxen, which are very helpful to some patients. Doctors may prescribe stronger drugs for some patients after examining their pain levels. Clonazepam helps treat the anxiety and poor sleep that sometimes occur with myofascial pain syndrome. It must be used carefully because it can cause sleepiness and be habit-forming.
A wide variety of drugs have been shown to ease chronic pain. Some of the effective ones are given below:
- Pain relievers – many patients with chronic pain get some relief from common painkillers such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and analgesics like naproxen, ibuprofen, aspirin, and ketoprofen. These OTC or prescriptions are considered safe when managing chronic pain conditions.
- Anti-depressants – Several medications are approved by the food and drug administration (FDA) to help control chronic pain. These include clomipramine, desipramine, imipramine, nortriptyline, doxepin, and amitriptyline. Pain-relievers help by boosting the mood of patients who are depressed and helping relieve chronic pain. Other anti-depressant drugs to treat pain include duloxetine and venlafaxine, which are clinically tested and approved for treating pain caused by fibromyalgia
Therapy
1. Stretching – physical therapy may lead you through gentle exercises to help relieve myofascial pain, particularly in your neck. Many exercises strengthen the muscles surrounding your trigger point, and this will soothe the pain.
2. Massage – The massage on the affected area helps to relieve muscle cramps. The therapist uses long hand strokes along the muscle to release tension.
3.Heat – Applying heat via a hot pack or shower can help relieve muscle tension and reduce pain. Occasional muscle pain is normal if you are active or new to exercise. But if the pain lasts longer, consult your doctor immediately.
Given all the ways chronic muscle pain can be controlled, speak to your doctor to know which treatment or combination of treatments makes sense for your chronic muscle pain.
Read More: The Benefits Of Outdoor Exercise For Mental Health
admin
Latest posts by admin (see all)
- What is Triluma Cream? Uses, Benefits, and How It Works for Skin - December 26, 2024
- What Causes Dark Spots? Understanding the Science of Hyperpigmentation and How Skin Lightening Products Help - December 26, 2024
- Tretinoin Gel vs. Cream: Which Formulation is Right for Your Skin? - December 20, 2024